Ford’s 7.3 powerstroke for sale is among the best diesel engine ever produced. Learn more about this amazing power engine in our article below typestrucks.com!
Best 7.3 Powerstroke for Sale Near Me!

One of the most notable specs you often find in Ford trucks or any type of large vehicles are 7.3 Powerstroke engine. A lot of Ford truck users testify that this 7.3 powerstroke for sale is the best of all. From 1994 until 2004, the Ford 7.3L Powerstroke engine was manufactured. Over the course of the 7.3L Powerstroke engine’s ten-year production run, more than 2 million of them were produced. Including in van chassis short buses, Ford employed the 7.3L Powerstroke to compete head-to-head with GM and Chrysler heavy-duty engine versions. Here are several interesting facts you need to know about 7.3 powerstroke engine for sale.
7.3L Powerstroke Engine’s Overview
Before you look for powerstroke engine for sale, you might want to learn a glimpse about its history first. The 7.3L Power Stroke was Ford’s first turbo-diesel engine from Navistar. The electronically regulated, direct injection engine had a diameter and stroke of 4.11 inches and a displacement of 444 cubic inches when it left the factory. It also had 210 horsepower and 425 lb-ft of torque. The 6.0L Power Stroke, Ford’s second turbo-diesel engine produced by Navistar, went on sale for the model year 2003.5. It had a bore and stroke of 3.74 inches and a displacement of 365 cubic inches, producing 325 horsepower and 560 lb-ft of torque.
However, it didn’t take long for the public to become aware of all of the 6.0L engine’s issues: blown head gaskets, cracked EGR coolers, failed EGR valves, sticking turbos, and bad injectors, to name a few. This was due to persistent recalls, numerous technical service bulletins, and the all-powerful word-of-mouth. The most recent 7.3 powerstroke for sale is said to have resolved all of the issues.
The Navistar International T444E, which also provided power to Type C school buses and other substantial commercial vehicles, was the basis for the 7.3L Power Stroke diesel engine. They have the same cast iron engine block, but they have different power control modules, which give the two engines different power ratings.

For instance, the Ford’s 7.3 obs powerstroke for sale diesel engine could provide 525 lb-ft of torque, while the T444E diesel engine could produce up to 620 lb-ft of torque for buses. The T444E diesel engine was outperformed in terms of horsepower by the 7.3L Power Stroke diesel engine. In addition, there were differences between the two engines’ water pumps, turbochargers, and several sensors.
7.3L Powerstroke Engine’s Paired Transmissions
Depending on the model year, a number of different transmissions were connected to the 7.3 obs powerstroke for sale diesel engine. The engine was paired to both a Ford E40D 4-speed automatic and a ZF Friedrichshafen S5-47 5-speed manual transmission from 1994 to 1998. Ford 4R110 4-speed automatic transmission and ZF Friedrichshafen S6-650 6-speed manual transmission were used to power the engine from 1999 to 2004.
7.3L Powerstroke Engine’s Towing Capacity

The next interesting aspect about this engine is about obs 7.3 powerstroke for sale’s towing capacity. The 7.3L Power Stroke diesel engine’s ability to tow was based on whether the cab had a two-wheel drive or four-wheel drive layout. Peak towing weight for a 4-wheel drive vehicle was 12,500 pounds, and the towing weight with a fifth wheel is 13,900 pounds.
7.3L Powerstroke Engine’s Life Expectancy
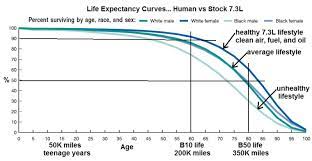
Before you search for 7.3 powerstroke for sale near me, the 7.3L Power Stroke diesel engine is renowned for lasting longer than gasoline ones. According to mechanics, a properly maintained diesel engine could travel at least 350,000 kilometers. Fewer 7.3L Power Stroke diesel engines are said to have reached 500,000 miles when properly maintained.
7.3L Powerstroke Power Engine vs 6.0L Powerstroke
While 7.3 Powerstroke Power Engine boast more power and less problematic, Ford has decided to use 6.0L Powerstroke instead. The decision was made by Ford who determined that the 6.0L engine would be the most effective way to comply with the new regulations because it would allow for lower NOx emissions criteria to be put into force in 2004. EGR, a more effective fuel injection system, and a variable geometry turbocharger would all be included in the 365-cubic-inch V8.
There was no certainty that the 7.3L’s core construction and design would have survived exhaust gas recirculation or been modified to produce much more than 300 horsepower. Keep in mind that the 7.3L had a 210 horsepower rating when it first appeared in mid-1994. Even then, people can easily find 7.3 powerstroke for sale near me.
Ford need a newer, more potent engine by 2003. The 7.3L had previously undergone five upgrades only to reach the 275 horsepower and 525 pound-feet threshold, and it was still lacking behind the 300 horsepower 6.6L Duramax introduced by GM in 2001. The 6.0L engine had four valves per cylinder, a higher pressure, hydraulically operated injection system, and it came with 325 horsepower and 560 lb-ft of torque and was raised to 570 lb-ft starting in 2005.
However, the 6.0L Power Stroke diesel engine was regarded as one of the most problematic engines in the Power Stroke diesel engine brand line, despite its cutting-edge technology. The emissions control systems and/or a lack of maintenance were the main causes of many of the problems with the 6.0L Power Stroke diesel engine.
EGR clogging and cooling issues, failures of the oil cooler and high-pressure oil system, various electrical problems, and head bolt and head gasket failures were all frequent issues. Over time, the engine problems got worse, resulting in expensive warranty repairs, manufacturer buybacks, and civil lawsuits against Ford. Ford’s 6.0L Power Stroke engine’s production ceased in 2012. In contrast, mechanics claim that problems emerged from 7.3L diesel engine can be solved quickly and doesn’t cost you fortune.
However, if you’re planning to purchase 7.3 powerstroke for sale there are several problems that might arise, such as:
- Camshaft Position Sensor (CPS) failure: The engine’s computer (PCM), which regulates the camshaft position and speed, receives the information from the CPS sensor and modifies the fuel delivery. The PCM does not receive the signal to give fuel if the sensor malfunctions. Engine stalls or no-starts are the end outcome. The most frequent failure point that mechanics describe is this problem. Fuel leaks can be caused by cracks appearing in the fuel housing (or fuel bowl). The gasoline system’s pressure and heat might degrade the cap and cause cracks that could lead to leaks.
- Leaky fuel filter housing: Fuel leaks can be caused by cracks appearing in the fuel housing (or fuel bowl). The gasoline system’s pressure and heat might degrade the cap and cause cracks that could lead to leaks.
- Lift pump problems: The engine cannot start if the lift pump fails. Before starting the engine and while cranking, check the fuel bowl. Fill the fuel bowl with clean fuel if it is empty. If it runs, change the pump.
- Injector Control Pressure (ICP) sensor: The engine cuts in and out due to a malfunctioning sensor. If the ICP connector shows signs of oil, the sensor may be damaged or close to failing. It is advised to replace the ICP sensor pigtail as well if oil has penetrated the wires.
- Injector Driver Module (IDM): The engine may stall or run rough if these modules malfunction or become wet. Look for moisture or water penetration, broken wiring, or both.
Read Also:

